分位点回帰#
分位点\(\tau\)における条件付分位関数を
と表す。ここで\(F_y^{-1}(\tau | X_i)\)は\(y\)において\(X_i\)に条件づけられた\(y_i\)の分布関数である(\(F_y^{-1}(\tau | X_i) = \inf \{ y: F_y(y|X_i) \geq \tau \}\))。
例えば\(\tau = 0.1\)のとき、\(Q_\tau(y_i | X_i)\)は\(y_i\)の下位10分位である。
標準的な回帰モデルは二乗誤差\((y_i - m(X_i))^2\)の和や期待値を最小化するようにモデル\(m(X_i)\)を学習して条件付き期待値\(E(y_i|X_i)\)を予測する
分位点回帰 (quantile regression)モデルはpinball loss\(\rho_{\tau}(y_i - q(X_i))\)の和や期待値を最小化するようにモデル\(q(X_i)\)を学習させ、条件付き分位関数\(Q_{\tau}(y_i|X_i) = F^{-1}_y(\tau|X_i)\)を予測する
pinball lossは \(\tau\)-tiled absolute value function や 検定関数(check function)とも呼ばれる(グラフを描くとチェックマークに似てるため)
あるいは
あるいは
と書かれる
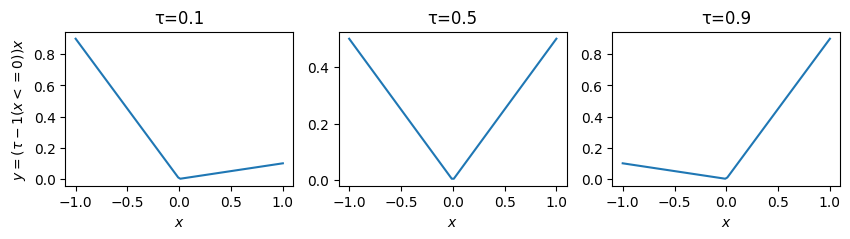
なお、pinball lossは\(\tau=0.5\)のとき
と、絶対誤差と比例する形になる。
絶対誤差の和を目的関数にとった線形モデルは統計学においてleast absolute deviations (LAD) と呼ばれ、その解は条件付き中央値になる

分位点回帰モデルの実践#
LightGBMでのquantile regression#
目的関数をbinball lossにすればいいだけなので他のアルゴリズムでも実行できる

from sklearn.metrics import d2_pinball_score, make_scorer
d2_pinball_score_09 = make_scorer(d2_pinball_score, alpha=0.9)
d2_pinball_score_09(model, X, y)
0.48475107952573926