Differential Item Functioning (DIF)#
概要#
Differential Item Functioning (DIF: 特異項目機能) とは、同じ能力を持つ異なる集団の受験者が、特定のテスト項目に対して異なる正答確率を示す現象である。
例えば、同じ数学的能力を持つ男女が、ある文章題に対して異なる正答率を示す場合、その項目にはDIFが存在する可能性がある。これは項目の内容が一方の集団に有利に働いていることを示唆し、テストの公平性(fairness)に関わる重要な問題である。
IRT文脈における Uniform DIF (Differential Item Functioning) は、 「潜在能力 \(\theta\) の全域にわたって、特定の群に対して一方向に“難易度がシフトしている”項目バイアス」を意味します。
定義(2PLMベース)#
Uniform DIF の仮定#
Uniform DIFでは
すなわち discrimination は 群不変 であり、
のように 困難度のみが群ごとに一定量シフト します。
したがって:
幾何学的解釈(ICC上)#
Uniform DIFがある場合:
ICC(Item Characteristic Curve)の傾きは同じ
ICCは 水平方向に平行移動
つまり:
群 |
ICC |
|---|---|
Group 0 |
baseline |
Group 1 |
baseline を \(\delta_j\) だけ左 or 右にシフト |
能力水準に依存せず:
すべての \(\theta\) において一方の群が一貫して有利 or 不利
Non-Uniform DIFとの違い(重要)#
Non-Uniform DIFでは:
となり、
となるため、
ICCの傾きが群で異なる
曲線が交差する(crossing ICC)
DIF効果が \(\theta\) に依存
階層ベイズでの実装(あなたのケース:複層ガラス×region)#
あなたがやろうとしている:
b_glass_base
b_glass_region
は、まさに Uniform DIF の典型的な
baseline + group-specific deviation
parameterization です。
数式で書くと:
したがって:
これは
regionごとの difficulty random effect
ICCの平行移動のみを許容
という意味で、Hierarchical Uniform DIF model になっています。
実務的解釈(不動産設備IRT)#
たとえば「複層ガラス」項目において:
北海道では標準装備 → 実質的に“易しい”
沖縄では希少 → 実質的に“難しい”
という climate-driven DIF は:
ability(住宅品質)が同じでも 地域により「付いている確率」が一様に変わる
= 典型的な Uniform DIF
であり、あなたの「気温カテゴリ × 設備」モデリング方針と整合します。
必要なら、GPCM/GRMでのUniform DIF(threshold shift)の定式化も展開します。
2PLモデルを考える:
ここで
\(a_j\) : 識別力(discrimination)
\(b_{jg}\) : 群 \(g\) における困難度(difficulty)
DIFの種類#
DIFには2種類ある:
Uniform DIF(均一DIF)
Non-uniform DIF(非均一DIF)
Uniform DIF(均一DIF)#
能力レベルに関わらず、一方の集団が常に有利(または不利)である場合。パラメータでいうと項目困難度 \(b\) が集団間で異なる状況。
例えば2母集団(グループ\(g\in\{1,2\}\))いるとして、\(b_{j, 1} \neq b_{j, 2}\)であるということ。
あるいは、ベースラインからの差分\(\delta\)があると表現する:\(b_{j 2}=b_{j 1}+\delta_j\)
ただし、識別力\(a_{j g}\)はグループ間で一定だとする:\(a_{j 1}=a_{j 2} = \cdots = a_{j G}\)
Non-uniform DIF(非均一DIF)#
集団間の差が能力レベルによって変化する場合。低能力では集団Aが有利だが、高能力では集団Bが有利になるなど。IRTでは識別力パラメータ \(a\) が集団間で異なる状況に対応する。
DIF検出手法#
Mantel-Haenszel法#
最も広く使用されているDIF検出手法の一つ。能力の代理指標として総得点を用い、各得点層で2×2の分割表を作成し、集団間の正答オッズ比を検定する。
Mantel-Haenszel統計量:
ここで \(A_k\) は得点層 \(k\) における参照群の正答者数、\(E(A_k)\) はその期待値。
共通オッズ比の推定値:
ETSでは、この対数を変換したDelta尺度(MH D-DIF)がよく使われる:
ロジスティック回帰法#
項目への正答を目的変数、能力(総得点)と集団を説明変数とするロジスティック回帰を用いる方法。
\(\theta\): 能力(または総得点)
\(G\): 集団を示すダミー変数
\(\beta_2 \neq 0\): Uniform DIFの存在
\(\beta_3 \neq 0\): Non-uniform DIFの存在
この方法の利点は、Uniform DIFとNon-uniform DIFを同時に検出できることである。
IRT法#
各集団で別々にIRTモデルを推定し、等化して尺度を揃えたのち、項目パラメータの差を検定する方法。
Lord’s \(\chi^2\) 検定:
ここで \(\hat{\boldsymbol{\xi}}\) は項目パラメータのベクトル、\(\hat{\boldsymbol{\Sigma}}\) はその共分散行列の推定値。
SIBTEST#
Shealy & Stout (1993) が開発した、多次元性に基づくDIF検出法。項目をアンカー項目(DIFがないと仮定)と検討項目に分け、条件付き期待得点の差を検定する。
Pythonでの実装#
difNLR パッケージ(R)#
Rには difR や difNLR など、DIF分析に特化したパッケージがある。
library(difNLR)
# Mantel-Haenszel法
difMH(Data, group, focal.name = 1)
# ロジスティック回帰法
difLogistic(Data, group, focal.name = 1, type = "both")
Pythonによる実装例#
PythonでのDIF分析は、statsmodels を用いたロジスティック回帰や、scipy.stats を用いたMantel-Haenszel検定で実装できる。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy import stats
import statsmodels.api as sm
from statsmodels.formula.api import logit
def mantel_haenszel_dif(response: np.ndarray, group: np.ndarray, total_score: np.ndarray):
"""
Mantel-Haenszel法によるDIF検出
Parameters
----------
response : np.ndarray
項目への応答(0/1)
group : np.ndarray
集団(0: 参照群, 1: 焦点群)
total_score : np.ndarray
総得点(能力の代理指標)
Returns
-------
dict
MH統計量、p値、共通オッズ比、MH D-DIF
"""
# 得点層ごとに分割表を作成
unique_scores = np.unique(total_score)
A_sum = 0 # 参照群・正答
B_sum = 0 # 参照群・誤答
C_sum = 0 # 焦点群・正答
D_sum = 0 # 焦点群・誤答
numerator = 0
denominator = 0
expected_A = 0
var_A = 0
for score in unique_scores:
mask = total_score == score
A = np.sum((group[mask] == 0) & (response[mask] == 1)) # 参照群・正答
B = np.sum((group[mask] == 0) & (response[mask] == 0)) # 参照群・誤答
C = np.sum((group[mask] == 1) & (response[mask] == 1)) # 焦点群・正答
D = np.sum((group[mask] == 1) & (response[mask] == 0)) # 焦点群・誤答
N = A + B + C + D
if N == 0:
continue
n1 = A + B # 参照群の人数
n2 = C + D # 焦点群の人数
m1 = A + C # 正答者数
m2 = B + D # 誤答者数
# オッズ比の計算用
numerator += A * D / N
denominator += B * C / N
# MH統計量の計算用
expected_A += n1 * m1 / N
var_A += n1 * n2 * m1 * m2 / (N**2 * (N - 1)) if N > 1 else 0
# 共通オッズ比
alpha_mh = numerator / denominator if denominator > 0 else np.nan
# MH D-DIF(ETS Delta尺度)
mh_d_dif = -2.35 * np.log(alpha_mh) if alpha_mh > 0 else np.nan
# MHカイ二乗統計量
observed_A = np.sum((group == 0) & (response == 1))
chi2_mh = (abs(observed_A - expected_A) - 0.5)**2 / var_A if var_A > 0 else np.nan
p_value = 1 - stats.chi2.cdf(chi2_mh, df=1)
return {
'chi2_mh': chi2_mh,
'p_value': p_value,
'alpha_mh': alpha_mh,
'mh_d_dif': mh_d_dif
}
def logistic_regression_dif(response: np.ndarray, group: np.ndarray, total_score: np.ndarray):
"""
ロジスティック回帰法によるDIF検出
Parameters
----------
response : np.ndarray
項目への応答(0/1)
group : np.ndarray
集団(0: 参照群, 1: 焦点群)
total_score : np.ndarray
総得点(能力の代理指標)
Returns
-------
dict
Uniform DIF検定結果、Non-uniform DIF検定結果
"""
df = pd.DataFrame({
'response': response,
'group': group,
'score': total_score,
'interaction': group * total_score
})
# Model 1: 能力のみ
model1 = logit('response ~ score', data=df).fit(disp=0)
# Model 2: 能力 + 集団(Uniform DIFの検定)
model2 = logit('response ~ score + group', data=df).fit(disp=0)
# Model 3: 能力 + 集団 + 交互作用(Non-uniform DIFの検定)
model3 = logit('response ~ score + group + score:group', data=df).fit(disp=0)
# Uniform DIF: Model 1 vs Model 2
lr_uniform = -2 * (model1.llf - model2.llf)
p_uniform = 1 - stats.chi2.cdf(lr_uniform, df=1)
# Non-uniform DIF: Model 2 vs Model 3
lr_nonuniform = -2 * (model2.llf - model3.llf)
p_nonuniform = 1 - stats.chi2.cdf(lr_nonuniform, df=1)
# Total DIF: Model 1 vs Model 3
lr_total = -2 * (model1.llf - model3.llf)
p_total = 1 - stats.chi2.cdf(lr_total, df=2)
return {
'uniform_dif': {
'chi2': lr_uniform,
'p_value': p_uniform,
'coefficient': model2.params.get('group', np.nan)
},
'nonuniform_dif': {
'chi2': lr_nonuniform,
'p_value': p_nonuniform,
'coefficient': model3.params.get('score:group', np.nan)
},
'total_dif': {
'chi2': lr_total,
'p_value': p_total
}
}
シミュレーションデータによる検証#
def simulate_dif_data(
n_reference: int = 500,
n_focal: int = 500,
n_items: int = 20,
dif_items: list[int] = None,
dif_magnitude: float = 0.5,
seed: int = 42
):
"""
DIFを含むシミュレーションデータを生成
Parameters
----------
n_reference : int
参照群の人数
n_focal : int
焦点群の人数
n_items : int
項目数
dif_items : list[int]
DIFを持つ項目のインデックス
dif_magnitude : float
DIFの大きさ(困難度パラメータの差)
seed : int
乱数シード
Returns
-------
tuple
応答データ、集団、総得点、真のDIF項目
"""
np.random.seed(seed)
if dif_items is None:
dif_items = [0, 1] # 最初の2項目にDIFを設定
n_total = n_reference + n_focal
# 能力パラメータ(両群とも標準正規分布)
theta = np.concatenate([
np.random.normal(0, 1, n_reference),
np.random.normal(0, 1, n_focal)
])
# 集団
group = np.concatenate([np.zeros(n_reference), np.ones(n_focal)]).astype(int)
# 項目パラメータ(1PLMを仮定)
b = np.random.uniform(-2, 2, n_items)
# 応答データの生成
responses = np.zeros((n_total, n_items))
for j in range(n_items):
b_j = b[j]
# DIF項目の場合、焦点群に対して困難度を変更
if j in dif_items:
b_effective = np.where(group == 1, b_j + dif_magnitude, b_j)
else:
b_effective = b_j
# 正答確率(1PLM)
prob = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-(theta - b_effective)))
responses[:, j] = (np.random.random(n_total) < prob).astype(int)
# 総得点
total_score = responses.sum(axis=1)
return responses, group, total_score, dif_items
# シミュレーションデータの生成
responses, group, total_score, true_dif_items = simulate_dif_data(
n_reference=500,
n_focal=500,
n_items=20,
dif_items=[0, 1],
dif_magnitude=0.8
)
print(f"データサイズ: {responses.shape}")
print(f"参照群: {np.sum(group == 0)}, 焦点群: {np.sum(group == 1)}")
print(f"真のDIF項目: {true_dif_items}")
データサイズ: (1000, 20)
参照群: 500, 焦点群: 500
真のDIF項目: [0, 1]
# 各項目についてDIF検出を実行
results = []
for j in range(responses.shape[1]):
# 検討項目を除いた総得点を計算
score_without_item = total_score - responses[:, j]
mh_result = mantel_haenszel_dif(responses[:, j], group, score_without_item)
lr_result = logistic_regression_dif(responses[:, j], group, score_without_item)
results.append({
'item': j + 1,
'true_dif': j in true_dif_items,
'mh_chi2': mh_result['chi2_mh'],
'mh_p': mh_result['p_value'],
'mh_d_dif': mh_result['mh_d_dif'],
'lr_uniform_p': lr_result['uniform_dif']['p_value'],
'lr_nonuniform_p': lr_result['nonuniform_dif']['p_value'],
'lr_total_p': lr_result['total_dif']['p_value']
})
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results)
results_df
| item | true_dif | mh_chi2 | mh_p | mh_d_dif | lr_uniform_p | lr_nonuniform_p | lr_total_p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | True | 20.471697 | 0.000006 | -1.572459 | 0.000002 | 0.159701 | 0.000004 |
| 1 | 2 | True | 12.660260 | 0.000374 | -1.321688 | 0.000183 | 0.080293 | 0.000198 |
| 2 | 3 | False | 0.107729 | 0.742745 | 0.130585 | 0.586662 | 0.569574 | 0.733820 |
| 3 | 4 | False | 0.001341 | 0.970788 | -0.036401 | 0.984099 | 0.284134 | 0.563379 |
| 4 | 5 | False | 4.178016 | 0.040952 | 0.909406 | 0.037480 | 0.638891 | 0.102866 |
| 5 | 6 | False | 1.783816 | 0.181681 | 0.579566 | 0.074110 | 0.983400 | 0.202909 |
| 6 | 7 | False | 2.191538 | 0.138771 | -0.701271 | 0.157806 | 0.908294 | 0.366339 |
| 7 | 8 | False | 0.212713 | 0.644649 | -0.172390 | 0.632513 | 0.614073 | 0.785466 |
| 8 | 9 | False | 0.246610 | 0.619472 | 0.191956 | 0.515535 | 0.009744 | 0.028667 |
| 9 | 10 | False | 1.824608 | 0.176766 | 0.564910 | 0.085535 | 0.128068 | 0.071639 |
| 10 | 11 | False | 0.078840 | 0.778876 | -0.119255 | 0.893427 | 0.634899 | 0.885404 |
| 11 | 12 | False | 0.216141 | 0.641996 | -0.190395 | 0.648446 | 0.206498 | 0.405823 |
| 12 | 13 | False | 0.000356 | 0.984946 | 0.017220 | 0.982344 | 0.084932 | 0.226685 |
| 13 | 14 | False | 0.192954 | 0.660469 | 0.190035 | 0.580818 | 0.693265 | 0.794340 |
| 14 | 15 | False | 1.025178 | 0.311294 | -0.426142 | 0.257368 | 0.422961 | 0.381949 |
| 15 | 16 | False | 0.552185 | 0.457426 | 0.323263 | 0.384877 | 0.823719 | 0.668750 |
| 16 | 17 | False | 0.686234 | 0.407448 | 0.288933 | 0.255636 | 0.435721 | 0.386787 |
| 17 | 18 | False | 0.888507 | 0.345882 | 0.380064 | 0.254879 | 0.342980 | 0.333601 |
| 18 | 19 | False | 0.109320 | 0.740919 | -0.127927 | 0.533438 | 0.333930 | 0.516481 |
| 19 | 20 | False | 0.454359 | 0.500272 | 0.247549 | 0.346342 | 0.931933 | 0.639508 |
# DIFが検出された項目
alpha = 0.05
print("=== Mantel-Haenszel法で検出されたDIF項目 ===")
detected_mh = results_df[results_df['mh_p'] < alpha]['item'].tolist()
print(f"検出された項目: {detected_mh}")
print(f"真のDIF項目: {[i+1 for i in true_dif_items]}")
print("\n=== ロジスティック回帰法で検出されたDIF項目 ===")
detected_lr = results_df[results_df['lr_total_p'] < alpha]['item'].tolist()
print(f"検出された項目: {detected_lr}")
print(f"真のDIF項目: {[i+1 for i in true_dif_items]}")
=== Mantel-Haenszel法で検出されたDIF項目 ===
検出された項目: [1, 2, 5]
真のDIF項目: [1, 2]
=== ロジスティック回帰法で検出されたDIF項目 ===
検出された項目: [1, 2, 9]
真のDIF項目: [1, 2]
DIFの解釈と対処#
DIFが検出された場合、以下のステップで対処する:
統計的有意性の確認: 多重比較の補正(Bonferroni補正など)を考慮
効果量の評価: MH D-DIFの絶対値が1.0以上で「中程度」、1.5以上で「大きい」とされる(ETS基準)
項目内容の精査: 専門家による項目レビューを実施し、DIFの原因を特定
対処の決定:
項目の削除
項目の修正
集団別の項目パラメータを使用
DIFの影響を考慮したスコアリング
DIFを考慮したスコアリング#
DIFが検出された場合、従来の単純な総得点(素点)は集団間の公平な比較を歪める可能性がある。ここでは、DIFの影響を適切に扱うスコアリング手法を紹介する。
アプローチ1: DIF項目の除外#
最も単純な方法は、DIFが検出された項目を除外して得点を算出することである。
ここで \(\mathcal{D}\) はDIF項目の集合である。この方法は直感的で実装が容易だが、項目数が減ることでテストの信頼性・測定精度が低下するという欠点がある。
アプローチ2: 集団別IRTパラメータによるスコアリング#
DIF項目については集団ごとに異なるパラメータを用い、非DIF項目については共通パラメータを用いて能力値を推定する方法である。2PLMの場合、受験者 \(i\) が集団 \(g\) に属するとき、各項目 \(j\) の正答確率は:
非DIF項目: \(b_{jR} = b_{jF} = b_j\)(共通パラメータ)
DIF項目: \(b_{jR} \neq b_{jF}\)(集団固有パラメータ)
能力値の推定には、集団に応じた適切なパラメータセットを用いてMLE(最尤推定)やEAP(期待事後推定)を行う。
この方法は全項目の情報を活用でき、DIFの影響を適切にモデル化できる。
アプローチ3: 期待得点調整#
Dorans & Holland (1993) に基づく方法で、DIF項目について参照群のパラメータで期待される得点に置き換えることで、焦点群に対するDIFの影響を補正する。
焦点群の受験者 \(i\) について、DIF項目 \(j\) の調整済みスコアは:
すなわち、焦点群パラメータでの期待得点と参照群パラメータでの期待得点の差だけ調整を加える。テスト全体の調整済み得点は:
この方法は項目を除外せずにDIFの影響のみを除去でき、かつ非DIF項目からの情報を保持できる。
アプローチ4: 多母集団IRTモデル#
最も理論的に洗練されたアプローチは、多母集団(multiple-group)IRTモデルを用いて全集団のデータを同時に推定することである。
このモデルでは:
アンカー項目(非DIF項目):全集団で共通の項目パラメータを推定
DIF項目:集団ごとに固有の項目パラメータを推定
能力分布:参照群を \(\theta_R \sim N(0, 1)\) に固定し、焦点群の能力分布 \(\theta_F \sim N(\mu_F, \sigma_F^2)\) を推定
全集団のデータを同時に用いるため推定精度が高く、等化が不要で、DIFの有無に関わらずすべての項目を活用できる。
実装例: 各スコアリング手法の比較#
先のシミュレーションデータを用いて、各スコアリング手法の効果を比較する。
from scipy.optimize import minimize_scalar
def irt_1pl_prob(theta: np.ndarray, b: float) -> np.ndarray:
"""1PLMの正答確率"""
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-(theta - b)))
def estimate_item_params_1pl(responses: np.ndarray, group: np.ndarray, dif_items: list[int]):
"""
集団別の項目パラメータを推定(1PLM、簡易版)
DIF項目は集団ごとに困難度を推定し、非DIF項目は全データで推定する。
Parameters
----------
responses : np.ndarray
応答行列 (n_persons x n_items)
group : np.ndarray
集団ラベル (0: 参照群, 1: 焦点群)
dif_items : list[int]
DIF項目のインデックス
Returns
-------
dict
集団ごとの困難度パラメータ
"""
n_items = responses.shape[1]
b_reference = np.zeros(n_items)
b_focal = np.zeros(n_items)
for j in range(n_items):
if j in dif_items:
# DIF項目: 集団別に推定
p_r = responses[group == 0, j].mean()
p_f = responses[group == 1, j].mean()
# ロジット変換で困難度を近似
b_reference[j] = -np.log(p_r / (1 - p_r)) if 0 < p_r < 1 else 0
b_focal[j] = -np.log(p_f / (1 - p_f)) if 0 < p_f < 1 else 0
else:
# 非DIF項目: 全データで推定
p_all = responses[:, j].mean()
b_common = -np.log(p_all / (1 - p_all)) if 0 < p_all < 1 else 0
b_reference[j] = b_common
b_focal[j] = b_common
return {'reference': b_reference, 'focal': b_focal}
def estimate_theta_mle(response_vector: np.ndarray, b: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""
1PLMのMLEによる能力推定
Parameters
----------
response_vector : np.ndarray
個人の応答パターン (n_items,)
b : np.ndarray
困難度パラメータ (n_items,)
Returns
-------
float
推定能力値
"""
def neg_log_lik(theta):
p = irt_1pl_prob(theta, b)
p = np.clip(p, 1e-10, 1 - 1e-10)
return -np.sum(response_vector * np.log(p) + (1 - response_vector) * np.log(1 - p))
result = minimize_scalar(neg_log_lik, bounds=(-4, 4), method='bounded')
return result.x
# 項目パラメータの推定
detected_dif_items = [i - 1 for i in detected_mh] # MH法で検出されたDIF項目(0-indexed)
item_params = estimate_item_params_1pl(responses, group, detected_dif_items)
n_persons = responses.shape[0]
n_items = responses.shape[1]
# --- 方法0: 素点(ベースライン)---
raw_scores = total_score
# --- 方法1: DIF項目除外 ---
non_dif_mask = [j for j in range(n_items) if j not in detected_dif_items]
purified_scores = responses[:, non_dif_mask].sum(axis=1)
# --- 方法2: 集団別IRTパラメータによるMLE推定 ---
theta_group_specific = np.zeros(n_persons)
for i in range(n_persons):
b = item_params['reference'] if group[i] == 0 else item_params['focal']
theta_group_specific[i] = estimate_theta_mle(responses[i], b)
# --- 方法3: 期待得点調整 ---
# まず共通パラメータでθを推定
b_common = np.zeros(n_items)
for j in range(n_items):
p_all = responses[:, j].mean()
b_common[j] = -np.log(p_all / (1 - p_all)) if 0 < p_all < 1 else 0
theta_common = np.array([estimate_theta_mle(responses[i], b_common) for i in range(n_persons)])
# 焦点群のDIF項目について調整
adjusted_scores = total_score.copy().astype(float)
for j in detected_dif_items:
focal_mask = group == 1
p_focal = irt_1pl_prob(theta_common[focal_mask], item_params['focal'][j])
p_reference = irt_1pl_prob(theta_common[focal_mask], item_params['reference'][j])
adjusted_scores[focal_mask] += (p_reference - p_focal)
print(f"検出されたDIF項目: {[i+1 for i in detected_dif_items]}")
print(f"項目数: 全{n_items}項目, DIF除外後{len(non_dif_mask)}項目")
検出されたDIF項目: [1, 2, 5]
項目数: 全20項目, DIF除外後17項目
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 10))
# 真の能力値を再構成
np.random.seed(42)
theta_true = np.concatenate([
np.random.normal(0, 1, 500),
np.random.normal(0, 1, 500)
])
scoring_methods = [
("Raw Score (素点)", raw_scores),
("Purified Score (DIF項目除外)", purified_scores),
("Group-Specific IRT (集団別IRT)", theta_group_specific),
("Adjusted Score (期待得点調整)", adjusted_scores),
]
for ax, (title, scores) in zip(axes.flat, scoring_methods):
ax.scatter(theta_true[group == 0], scores[group == 0], alpha=0.3, s=10, label='Reference')
ax.scatter(theta_true[group == 1], scores[group == 1], alpha=0.3, s=10, label='Focal')
ax.set_xlabel('True θ')
ax.set_ylabel('Score')
ax.set_title(title)
ax.legend()
fig.suptitle('各スコアリング手法と真の能力値の関係', fontsize=14, y=1.01)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 32032 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-7D20}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 28857 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-70B9}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 38917 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9805}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 30446 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-76EE}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 38500 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9664}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 22806 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5916}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 38598 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-96C6}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 22243 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-56E3}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 21029 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5225}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 26399 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-671F}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 24453 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5F85}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 24471 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5F97}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 35519 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-8ABF}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 25972 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-6574}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 21508 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5404}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12473 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER SU}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12467 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER KO}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12450 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER A}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12522 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER RI}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12531 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER N}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12464 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER GU}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 25163 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-624B}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 27861 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-6CD5}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12392 (\N{HIRAGANA LETTER TO}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 30495 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-771F}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 12398 (\N{HIRAGANA LETTER NO}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 33021 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-80FD}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 21147 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-529B}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 20516 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5024}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 38306 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-95A2}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/tmp/ipykernel_10343/3640317213.py:28: UserWarning: Glyph 20418 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-4FC2}) missing from current font.
plt.tight_layout()
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 32032 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-7D20}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 28857 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-70B9}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 38917 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9805}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 30446 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-76EE}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 38500 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-9664}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 22806 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5916}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 38598 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-96C6}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 22243 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-56E3}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 21029 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5225}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 26399 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-671F}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 24453 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5F85}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 24471 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5F97}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 35519 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-8ABF}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 25972 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-6574}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 21508 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5404}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12473 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER SU}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12467 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER KO}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12450 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER A}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12522 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER RI}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12531 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER N}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12464 (\N{KATAKANA LETTER GU}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 25163 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-624B}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 27861 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-6CD5}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12392 (\N{HIRAGANA LETTER TO}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 30495 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-771F}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 12398 (\N{HIRAGANA LETTER NO}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 33021 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-80FD}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 21147 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-529B}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 20516 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-5024}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 38306 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-95A2}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
/home/runner/work/notes/notes/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:170: UserWarning: Glyph 20418 (\N{CJK UNIFIED IDEOGRAPH-4FC2}) missing from current font.
fig.canvas.print_figure(bytes_io, **kw)
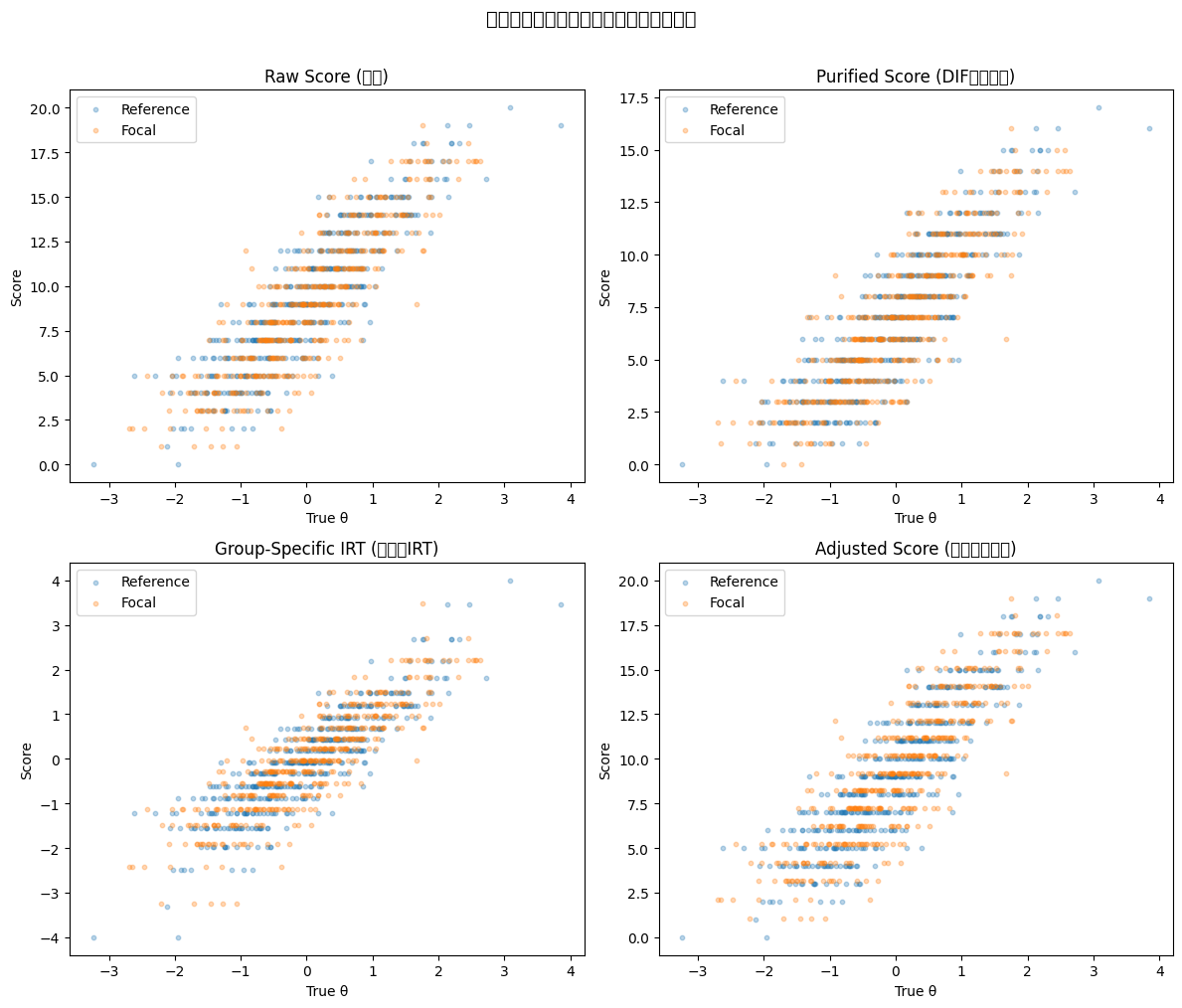
# 各手法の評価: 集団間の得点差(同じ能力を持つ場合の公平性)
print("=== 各スコアリング手法の集団間比較 ===\n")
for title, scores in scoring_methods:
mean_r = scores[group == 0].mean()
mean_f = scores[group == 1].mean()
corr_r = np.corrcoef(theta_true[group == 0], scores[group == 0])[0, 1]
corr_f = np.corrcoef(theta_true[group == 1], scores[group == 1])[0, 1]
print(f"--- {title} ---")
print(f" 平均得点: 参照群={mean_r:.3f}, 焦点群={mean_f:.3f}, 差={mean_r - mean_f:.3f}")
print(f" θとの相関: 参照群={corr_r:.3f}, 焦点群={corr_f:.3f}")
print()
=== 各スコアリング手法の集団間比較 ===
--- Raw Score (素点) ---
平均得点: 参照群=9.296, 焦点群=9.120, 差=0.176
θとの相関: 参照群=0.879, 焦点群=0.871
--- Purified Score (DIF項目除外) ---
平均得点: 参照群=6.936, 焦点群=6.956, 差=-0.020
θとの相関: 参照群=0.863, 焦点群=0.861
--- Group-Specific IRT (集団別IRT) ---
平均得点: 参照群=-0.041, 焦点群=-0.048, 差=0.008
θとの相関: 参照群=0.877, 焦点群=0.866
--- Adjusted Score (期待得点調整) ---
平均得点: 参照群=9.296, 焦点群=9.288, 差=0.008
θとの相関: 参照群=0.879, 焦点群=0.871
手法の選択指針#
手法 |
利点 |
欠点 |
推奨場面 |
|---|---|---|---|
DIF項目除外 |
実装が容易 |
情報損失、信頼性低下 |
DIF項目が少数の場合 |
集団別IRTパラメータ |
全項目の情報を活用 |
等化が必要、推定が複雑 |
IRTモデルが適合する場合 |
期待得点調整 |
素点スケールで調整可能 |
能力推定の精度に依存 |
素点での報告が必要な場合 |
多母集団IRT |
理論的に最も適切 |
実装が複雑、大標本が必要 |
大規模テスト |
実務的には、DIFが少数の項目にのみ見られ効果量が小さい場合には素点のままでも許容される場合がある。一方、DIFが多くの項目に見られるか効果量が大きい場合には、集団別IRTパラメータや多母集団IRTモデルの利用を検討すべきである。
参考文献#
Holland, P. W., & Wainer, H. (Eds.). (1993). Differential item functioning. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
DIFに関する包括的な教科書
Magis, D., Béland, S., Tuerlinckx, F., & De Boeck, P. (2010). A general framework and an R package for the detection of dichotomous differential item functioning. Behavior Research Methods, 42(3), 847-862.
RのdifRパッケージの論文。DIF検出手法の比較も行っている
Swaminathan, H., & Rogers, H. J. (1990). Detecting differential item functioning using logistic regression procedures. Journal of Educational Measurement, 27(4), 361-370.
ロジスティック回帰法によるDIF検出の基礎論文